- support@gmail.com
- Bangalore
Call Now 823-080-87678
Vascular Intervention
- Home
- Treatments
- Interventions in Vascular Malformations
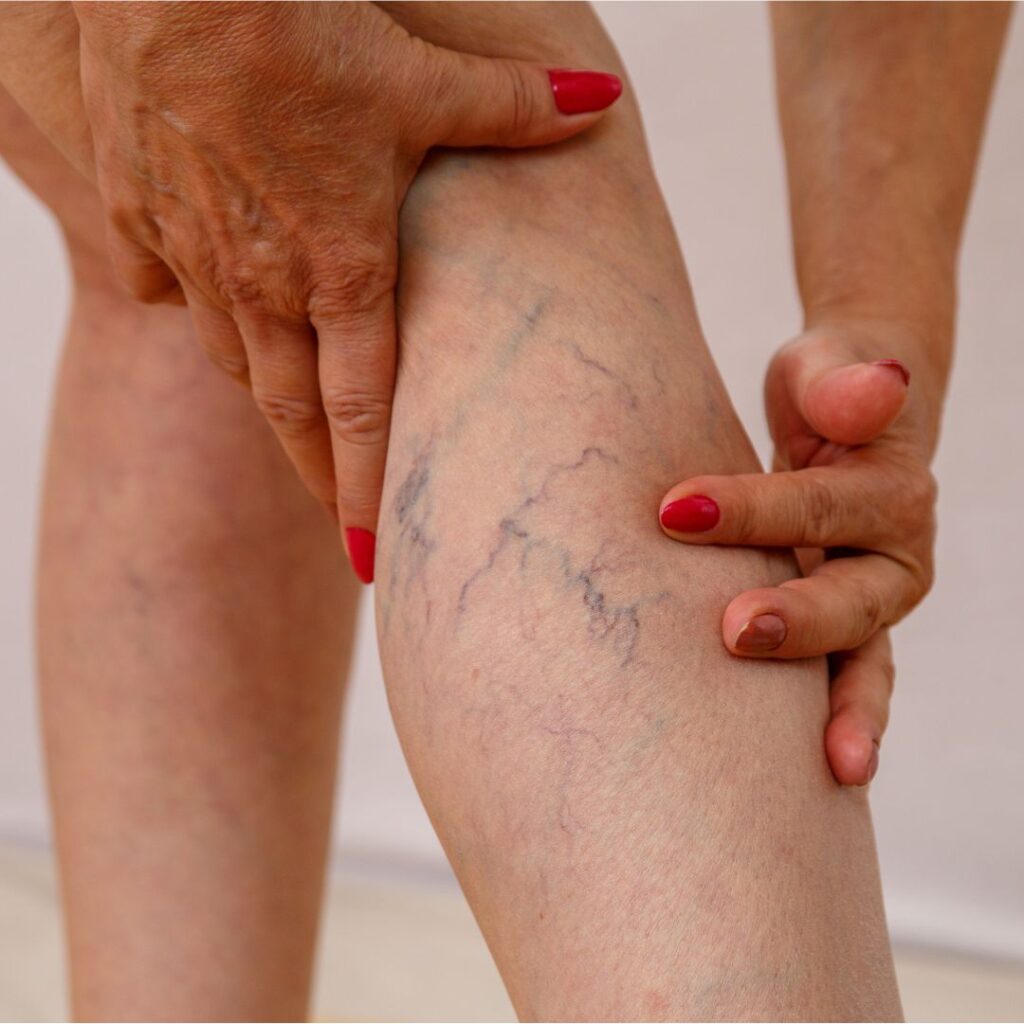
Vascular Interventions
Vascular malformations are abnormal clusters of blood vessels that can occur anywhere in the body, including the brain, spine, and extremities. These malformations are usually present from birth and can cause symptoms like pain, bleeding, or neurological issues.
Symptoms We Treat
- Bleeding or bruising
- Pain in the affected area
- Swelling in affected area
- Seizures or headaches
- Skin color changes
- Visible deformities
Causes
Congenital abnormalities in the vascular system, arteriovenous, venous, or lymphatic malformations.
Risks
Potential risks include bleeding, infection, or recurrence of the malformation.
ProcedureS
Embolisation
Sclerotherapy
Laser Therapy
Using focused light to reduce or remove superficial malformations.
Treatment Options
Surgical Resection
In some cases, surgery may be required to remove the malformation entirely.
Endovascular Therapy
Minimally invasive techniques to treat malformations from within the blood vessels.
Combined Treatments
Using a combination of embolisation and surgery for complex cases.
post Procedure Recovery
Recovery times vary depending on the procedure, but most patients can return to normal activities within a few days to a week. Follow-up care is essential to monitor the treated area for any signs of recurrence.
Success rate
The success rate of treating vascular malformations is high, particularly when using embolisation techniques. Success rates can range from 70% to 90%, depending on the size and location.
Some malformations may require multiple treatments depending on their size and complexity.
Most patients recover within a few weeks, with minimal restrictions on daily activities.
There is a risk of recurrence, but it is lower with minimally invasive techniques like embolisation.
